Security researchers have dissected a recently emerged ransomware strain named ‘Big Head’ that may be spreading through malvertising that promotes fake Windows updates and Microsoft Word installers.
Two samples of the malware have been analyzed before by cybersecurity company Fortinet, who looked at the infection vector and how the malware executes.
Today, Trend Micro published a technical report on Big Head that claiming that both variants and a third they sampled originate from a single operator who is likely experimenting with different approaches to optimize their attacks.
Faking a Windows update
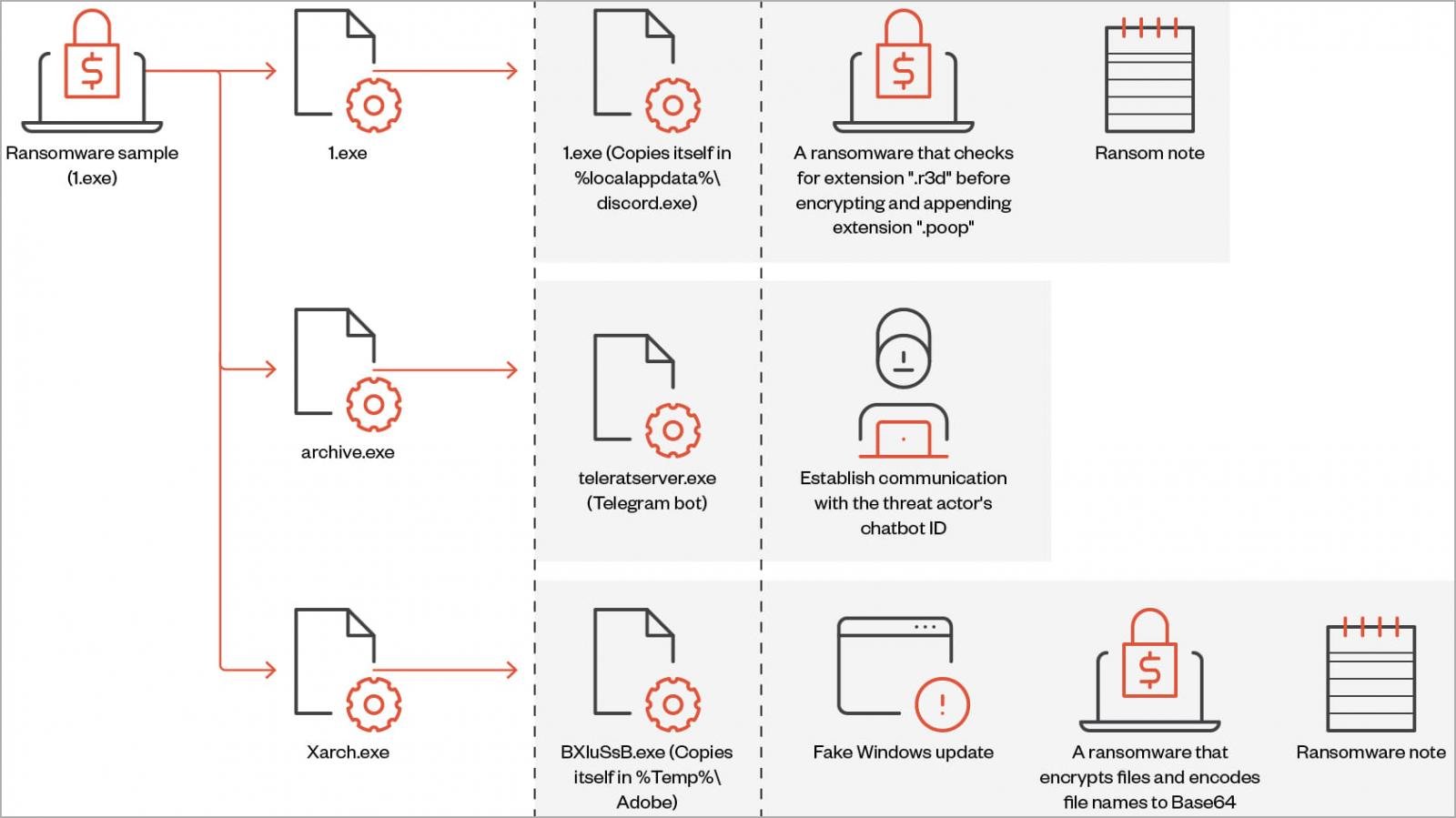
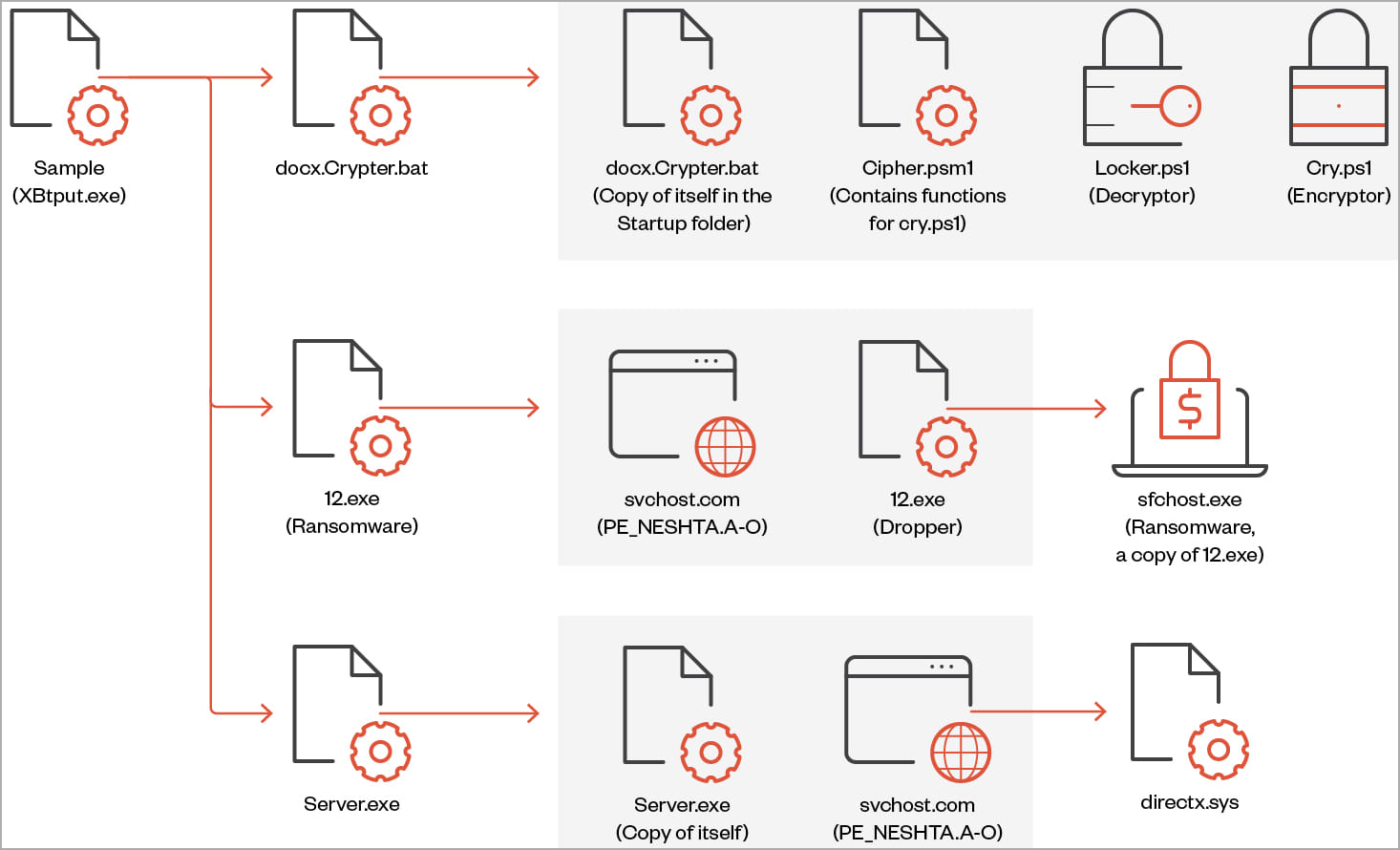
‘Big Head’ ransomware is a .NET binary that installs three AES-encrypted files on the target system: one is used to propagate the malware, another is for Telegram bot communication, and the third encrypts files and can also show the user a fake Windows update.
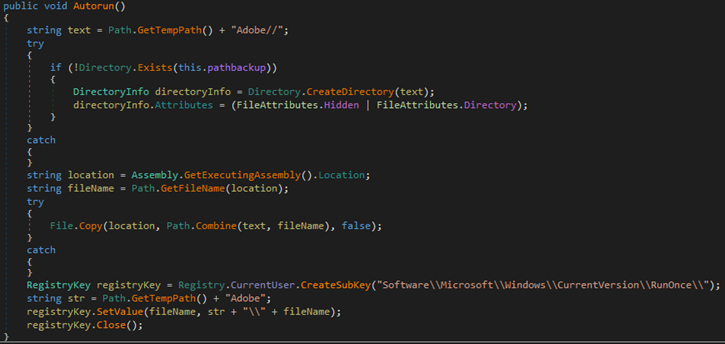
On execution, the ransomware also performs actions such as creating a registry autorun key, overwriting existing files if needed, setting system file attributes, and disabling the Task Manager.
Each victim is assigned a unique ID that’s either retrieved from the %appdata%\ID directory or it is generated using a random 40-character string.
The ransomware deletes shadow copies to prevent easy system restoration before encrypting the targeted files and appending a “.poop” extension to their filenames.

Also, Big Head will terminate the following processes to prevent tampering with the encryption process and to free up data that the malware should lock.
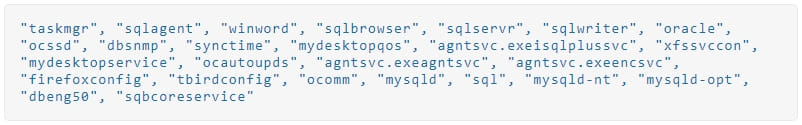
The Windows, Recycle Bin, Program Files, Temp, Program Data, Microsoft, and App Data directories are skipped from encryption to avoid rendering the system unusable.
Trend Micro has found that the ransomware checks if it runs on a virtual box, looks for the system language, and only proceeds to the encryption if it’s not set on that of a country member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (former Soviet states).

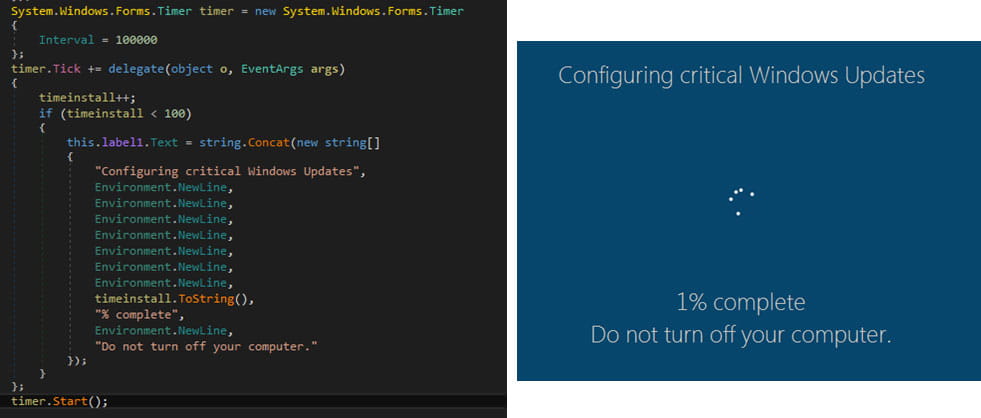
During the encryption, the ransomware displays a screen that purports to be a legitimate Windows update.
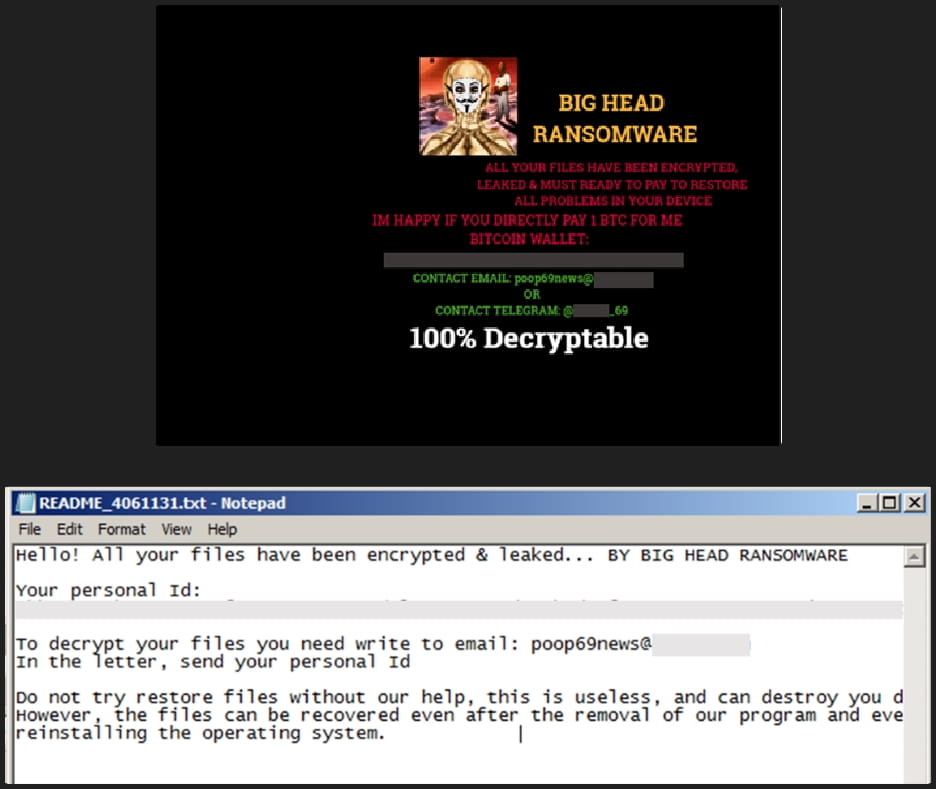
After the encryption process completes, the following ransom is dropped on multiple directories, and the victim’s wallpaper is also changed to alert of the infection.
Other variants
Trend Micro also analyzed two more Big Head variants, highlighting some key differences compared to the standard version of the ransomware.
The second variant maintains ransomware capabilities but also incorporates stealer behavior with functions to collect and exfiltrate sensitive data from the victim system.
The data that this version of Big Head can steal include browsing history, list of directories, installed drivers, running processes, product key, and active networks, and it can also capture screenshots.
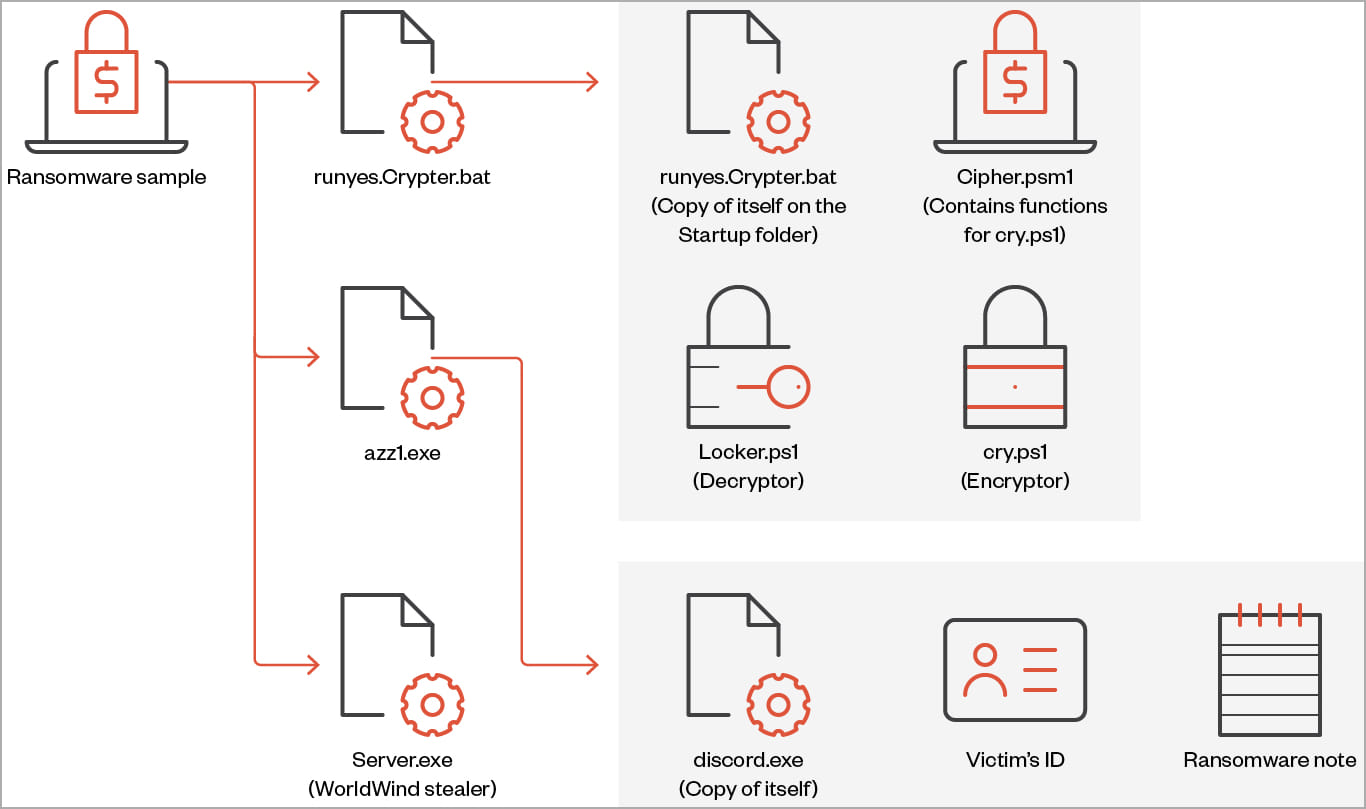
The third variant, discovered by Trend Micro, features a file infector identified as “Neshta,” which inserts malicious code into executables on the breached system.
Although the exact purpose of this is unclear, Trend Micro’s analysts speculate that it could be to evade detection that relies on signature-based mechanisms.
Notably, this variant uses a different ransom note and wallpaper from the other two, yet it is still tied to the same threat actor.
Conclusion
Trend Micro comments that Big Head is not a sophisticated ransomware strain, its encryption methods are pretty standard, and its evasion techniques are easy to detect.
Nevertheless, it appears to focus on consumers who can be fooled with easy tricks (e.g. fake Windows update) or they have difficulty understanding the safeguards necessary to steer away from cybersecurity risks.
The multiple variants in circulation suggest that the creators of Big Head are continuously developing and refining the malware, experimenting with various approaches to see what works best.