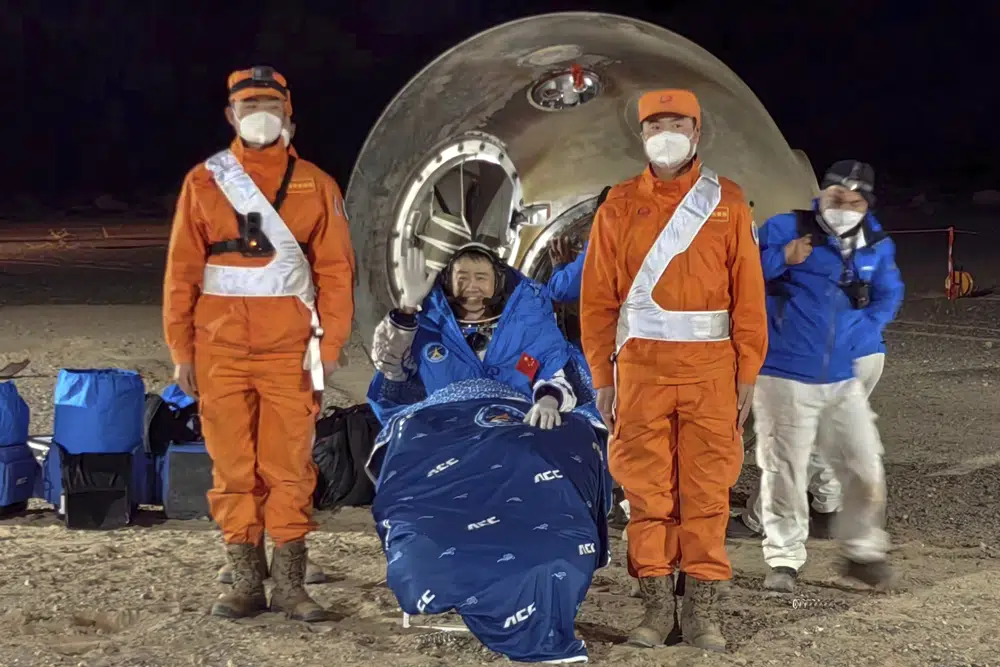
In this photo released by Xinhua News Agency, astronaut Chen Dong waves as he sits outside the re-entry capsule of the Shenzhou-14 manned space mission after it lands successfully at the Dongfeng landing site in northern China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Sunday, Dec. 4, 2022. Three Chinese astronauts landed in a northern desert on Sunday after six months working to complete construction of the Tiangong station, a symbol of the country’s ambitious space program, state TV reported. (Li Gang/Xinhua via AP)
BEIJING (AP) — Three Chinese astronauts landed in a northern desert on Sunday after six months working to complete construction of the Tiangong station, a symbol of the country’s ambitious space program, state TV reported.
A capsule carrying commander Chen Dong and astronauts Liu Yang and Cai Xuzhe touched down at a landing site in the Gobi Desert in northern China at approximately 8:10 p.m. (1210 GMT), China Central Television reported.
Prior to departure, they overlapped for almost five days with three colleagues who arrived Wednesday on the Shenzhou-15 mission for their own six-month stay, marking the first time China had six astronauts in space at the same time. The station’s third and final module docked with the station this month.
The astronauts were carried out of the capsule by medical workers about 40 minutes after touchdown. They were all smiles, and appeared to be in good condition, waving happily at workers at the landing site.
“I am very fortunate to have witnessed the completion of the basic structure of the Chinese space station after six busy and fulfilling months in space,” said Chen, who was the first to exit the capsule. “Like meteors, we returned to the embrace of the motherland.”
Liu, another of the astronauts, said that she was moved to see relatives and her fellow compatriots.
The three astronauts were part of the Shenzhou-14 mission, which launched in June. After their arrival at Tiangong, Chen, Liu and Cai oversaw five rendezvous and dockings with various spacecraft including one carrying the third of the station’s three modules.
They also performed three spacewalks, beamed down a live science lecture from the station, and conducted a range of experiments.
The Tiangong is part of official Chinese plans for a permanent human presence in orbit.
China built its own station after it was excluded from the International Space Station, largely due to U.S. objections over the Chinese space programs’ close ties to the People’s Liberation Army, the military wing of the ruling Communist Party.
With the arrival of the Shenzhou-15 mission, the station expanded to its maximum weight of 100 tons.
Without attached spacecraft, the Chinese station weighs about 66 tons — a fraction of the International Space Station, which launched its first module in 1998 and weighs around 465 tons.
With a lifespan of 10 to 15 years, Tiangong could one day be the only space station still up and running if the International Space Station retires by around the end of the decade as expected.
China in 2003 became the third government to send an astronaut into orbit on its own after the former Soviet Union and the United States.
China has also chalked up uncrewed mission successes: Its Yutu 2 rover was the first to explore the little-known far side of the moon. Its Chang’e 5 probe also returned lunar rocks to Earth in December 2020 for the first time since the 1970s, and another Chinese rover is searching for evidence of life on Mars.
Officials are reported to be considering an eventual crewed mission to the moon, although no timeline has been offered.
Copyright 2021 Associated Press. All rights reserved.