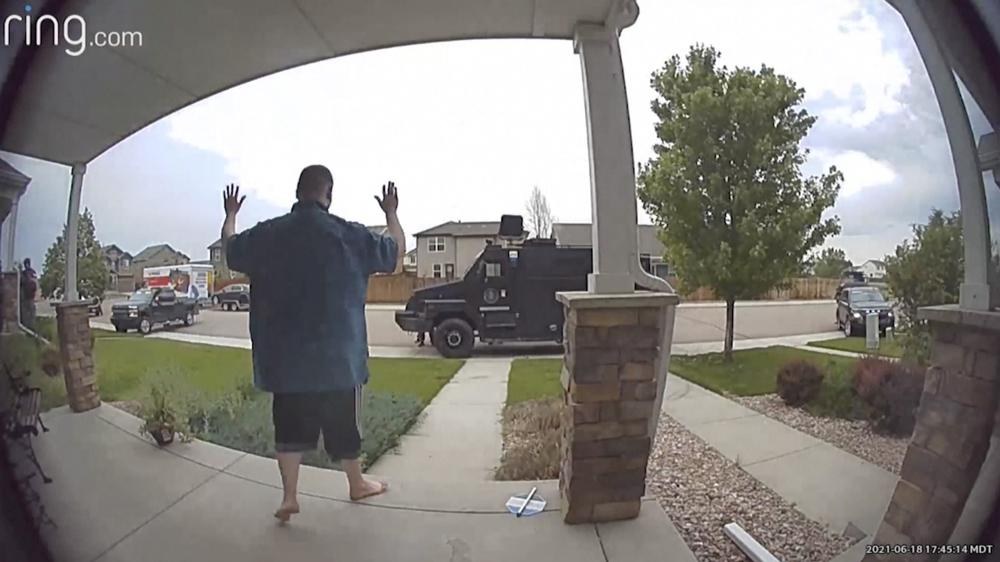
In this image from video provided by Leslie Bowman, Anderson Lee Aldrich surrenders to police at a home where his mother, Laura Voepel, was renting a room in Colorado Springs, Colo., on June 18, 2021. According to sealed law enforcement documents verified by The Associated Press, Aldrich’s actions brought SWAT teams and the bomb squad to the normally quiet neighborhood, forced the grandparents to flee for their lives and prompted the evacuation of 10 nearby homes to escape a possible bomb blast. (Leslie Bowman via AP)
DENVER (AP) — Authorities said the person who would later kill five at a Colorado gay nightclub was on the FBI’s radar a day before being arrested for threatening to kill family members, but agents closed out the case just weeks later.
The FBI’s disclosure about the tip, provided in a statement to The Associated Press, creates a new timeline for when law enforcement was first alerted to Anderson Lee Aldrich as a potential danger. The FBI did not say who gave the tip on June 17, 2021, or anything about the information that was provided.
The next day, law enforcement was alerted when Aldrich’s grandparents ran from their Colorado Springs home and called 911, saying Aldrich was building a bomb in the basement and had threatened to kill them. Details of the case remain sealed, but an arrest affidavit verified by the AP detailed how Aldrich was upset the grandparents were moving to Florida because it would get in the way of Aldrich’s plans to conduct a mass shooting and bombing.
The grandparents were concerned about Aldrich even before the 911 call, according to the document, with the grandmother telling authorities she and her husband had been “living in fear” because of Aldrich’s “recent homicidal threats toward them and others.”
In a story Sunday, The Denver Gazette cited an unidentified family member saying the grandfather called the FBI the day before the bomb threat. The shooting is the latest crime to raise questions about whether the FBI moves too soon to close cases involving people who have shown violent tendencies.
As part of the FBI’s probe, the agency said it coordinated with the El Paso County Sheriff’s Office, which had responded to the June 18, 2021, call from Aldrich’s grandparents and arrested Aldrich, now 22, on felony menacing and kidnapping charges. But about a month after getting the tip, the FBI closed its assessment of Aldrich, who is nonbinary and uses they/them pronouns.
“With state charges pending, the FBI closed its assessment on July 15, 2021,” the FBI said.
Those charges were later dropped for unknown reasons. Under Colorado law, cases that are dismissed by either prosecutors or a judge are automatically sealed to prevent people from having their lives ruined if they do not end up being prosecuted. Authorities have cited the law in refusing to answer questions about the case but a coalition of media organizations, including the AP, has asked the court to unseal the records. A hearing is planned for Thursday.
A spokesperson for the sheriff’s office, Sgt. Jason Garrett, declined to comment on the FBI’s statement or on whether his agency had any tips about Aldrich before their 2021 arrest, citing the sealing law.
The shooting at Club Q occurred more than a year later, just before midnight on Nov. 19, when Aldrich opened fire as soon as they entered the club, firing indiscriminately with an AR-15-style rifle while wearing a ballistic vest, according to an arrest affidavit that was written the day after the shooting but not unsealed until Wednesday evening. Aldrich killed five people and wounded 17 others before an Army veteran wrestled the attacker to the ground.
The affidavit does not provide any new information about what motivated Aldrich, but says they expressed remorse to medical staff shortly after the shooting and said they had been awake for four days, according to police officers guarding their room at the hospital. It doesn’t including anything more about what Aldrich may have told investigators.
The document also includes an image from the club’s surveillance video showing a blast coming out of the rifle barrel as Aldrich entered the club.
Aldrich’s mother told police that they were supposed to go to a movie at 10 p.m. that night, about two hours before the attack, but said Aldrich had left before then, saying they had to do quick errand.
The FBI is now helping to investigate the shooting. Xavier Kraus, a former neighbor of Aldrich and their mother, told the AP Wednesday that agents have interviewed him in recent days about a free speech website Aldrich created that has featured a series of violent posts, glorifying violence and racism.
“It was meant for people to go and pretty much say whatever they want with the exception of the two rules: No spamming and no child pornography,” Kraus said. “If I would have known what it was going to turn into, that would have struck a different chord with me.”
Kraus said that after the bomb threat charges were dropped, Aldrich began boasting about recovering the guns, and once showed Kraus two assault-style rifles, body armor and incendiary rounds.
Kraus said Aldrich “was talking about bullets that could pierce through police-grade armor.” He said it seemed like Aldrich hoped someone would break into their home.
An FBI assessment is the lowest level, least intrusive, and most elementary stage of an FBI inquiry. Such assessments are routinely opened after agents receive a tip, and investigators routinely face the challenge of sifting through which of the tens of thousands of tips received every year could yield a viable threat.
There have been several high-profile examples of the FBI having received information about a gunman before a mass shooting. A month before Nikolas Cruz killed 17 people at a Florida high school, the bureau received a warning that he had been talking about committing a mass shooting. A man who massacred 49 people at an Orlando nightclub in 2016 and another who set off bombs in the streets of New York City the same year had each been looked at by federal agents but officials later determined they did not warrant continued law enforcement scrutiny.
FBI guidelines meant to balance national security with civil liberties protections impose restrictions on the steps agents may take during the assessment phase. Agents, for instance, may analyze information from government databases and open-source internet searches, and can conduct interviews during an assessment. But they cannot turn to more intrusive techniques, such as requesting a wiretap or internet communications, without higher levels of approval and a more solid basis to suspect a crime.
More than 10,000 assessments are opened each year. Many are closed within days or weeks when the FBI concludes there’s no criminal or national security threat, or basis for continued scrutiny. The system is meant to ensure that a person who has not broken the law does not remain under perpetual scrutiny on a mere hunch — and that the FBI can reserve its resources for true threats.
___
Mustian reported from Colorado Springs. Associated Press writers Michael Balsamo and Lindsay Whitehurst contributed to this report from Washington.
There have been several high-profile examples of the FBI having received information about a gunman before a mass shooting. A month before Nikolas Cruz killed 17 people at a Florida high school, the bureau received a warning that he had been talking about committing a mass shooting. A man who massacred 49 people at an Orlando nightclub in 2016 and another who set off bombs in the streets of New York City the same year had each been looked at by federal agents but officials later determined they did not warrant continued law enforcement scrutiny.
FBI guidelines meant to balance national security with civil liberties protections impose restrictions on the steps agents may take during the assessment phase. Agents, for instance, may analyze information from government databases and open-source internet searches, and can conduct interviews during an assessment. But they cannot turn to more intrusive techniques, such as requesting a wiretap or internet communications, without higher levels of approval and a more solid basis to suspect a crime.
More than 10,000 assessments are opened each year. Many are closed within days or weeks when the FBI concludes there’s no criminal or national security threat, or basis for continued scrutiny. The system is meant to ensure that a person who has not broken the law does not remain under perpetual scrutiny on a mere hunch — and that the FBI can reserve its resources for true threats.
___
Mustian reported from Colorado Springs. Associated Press writers Michael Balsamo and Lindsay Whitehurst contributed to this report from Washington.
Copyright 2021 Associated Press. All rights reserved.