The coronavirus-induced lockdowns experienced by much of the world over winter has done little to scupper researchers’ desire to tinker and create.
In fact, the past three months saw the release of a variety of new hacking tools to make the lives of penetration testers, bug bounty hunters, and infosec hobbyists that little bit easier.
Here’s our roundup of the latest hacking tools for the first quarter of 2021:
Centris tackles supply chain woes by flagging modified open source components
A global team of researchers has developed a novel approach to the thorny problem of tracking the prolific reuse of open source components in software projects.
Centris draws on a component database spanning more than 80 billion lines of code to efficiently spot reused OSS components even when – unlike comparable existing tools – they are modified.
The tool has already been successful in surfacing longstanding vulnerabilities in hundreds of GitHub projects, the developers said.
Hashcat companion CrackQ adds GUI, analysis features to password-cracking platform
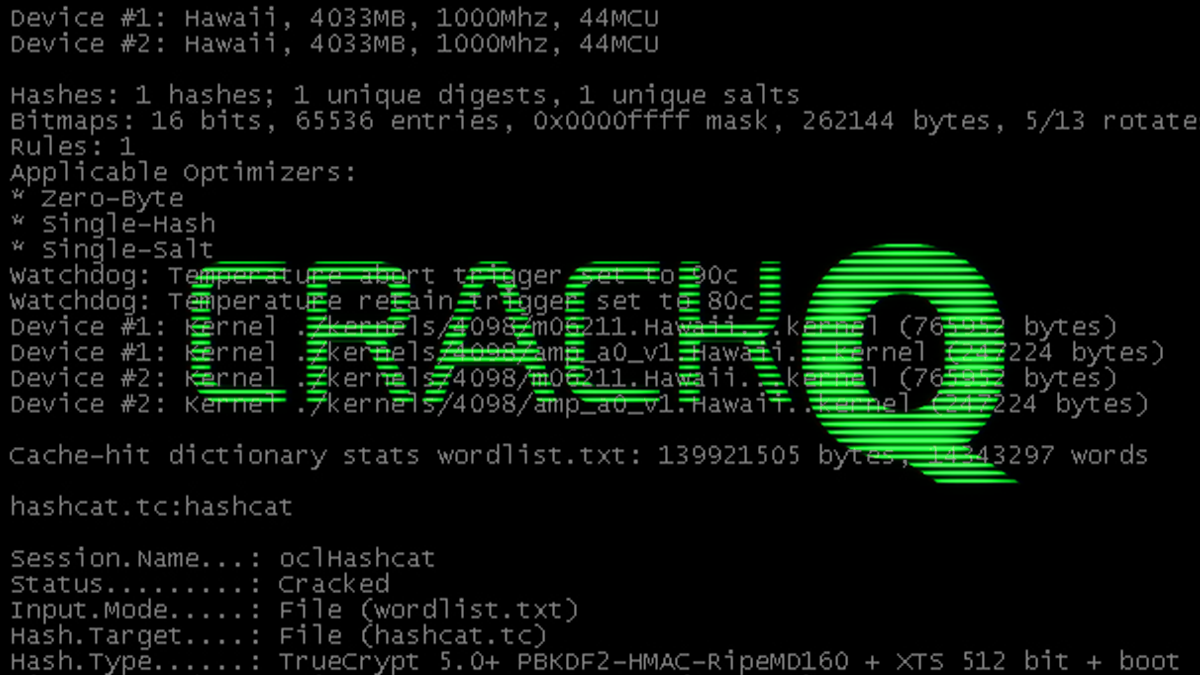
CrackQ provides a REST API and JavaScript graphical user interface (GUI) to interact with Hashcat, the password-cracking, command-line tool popular with offensive security researchers.
CrackQ developer Dan Turner told The Daily Swig that the project’s goal was to improve the efficiency of Hashcat, which leverages graphics cards to find the plaintext equivalent of hashed passwords.
The open source Python tool generates analysis reports and dashboards from Hashcat results, uses SAML2 authentication, has a server/client architecture, and is built using Docker containers.
Nzyme detects WiFi hijacking devices the moment they are ‘powered on and in range’

Nzyme was needed because existing wireless intrusion detection systems (IDS) were “easily spoofed” as well as broken by commercially available hacking tools, said the tool’s developer Lennart Koopmann.
Nzyme, which can be used as a portable tracker device, has built-in definitions for “out-of-the-box bandit” devices, such as the WiFi Pineapple and Pwnagotchi.
Detecting such devices the moment they are “powered on and in range”, the tool will bolster “your security posture in a notoriously under-secured and easy-to-attack environment like WiFi”, said Koopmann.
Regexploit hunts for ReDoS flaws in regex implementations

A new regex-scanning tool has been used by its architects to unearth multiple regular expression denial-of-service (ReDoS) vulnerabilities in popular NPM, Python, and Ruby dependencies.
Released in March, Regexploit extracts regular expressions and scans them for widespread security weaknesses that, if exploited, can “bring a server to its knees”, said Doyensec researcher Ben Caller.
“This is a much-needed tool, and it works well,” security researcher Somdev Sangwan told The Daily Swig. “Being an open source project, it will only get better with time.”
SerialDetector speeds up discovery of .Net deserialization bugs

A team of researchers has developed a new open source tool that can help automate the discovery of dangerous deserialization vulnerabilities in .Net applications.
SerialDetector has already netted the researchers bug bounties after helping them to unearth three critical vulnerabilities potentially leading to remote code execution in Microsoft’s Azure DevOps Server.
The researchers, from Sweden’s KTH Royal Institute of Technology, also used the tool to uncover object injection vulnerabilities in six other applications.
Read more about SerialDetector
Shorteners tool scours the web for exposed shortened URLs

Shorteners is a new online service that allows security researchers to search for exposed shortened URLs.
Known for their risks to security and privacy, shortened URLs are comparatively easy to brute-force, thanks to the lower character count which reduces the number of possibilities. These links also often contain sensitive documents.
Using Grayhat Warfare’s new service, users can search using keywords, filter by extensions, or browse any links that have been shortened from a specific domain.
Other hacking tools and related news this quarter:
More hacking tools and related news for the first quarter of 2021:
- Security researcher John Page has launched Malvuln.com, a pioneering malware vulnerability database.
- The Nmap project became the latest victim of Google’s ‘wrongful blocking’ of cybersecurity resources.
- In a wide-ranging interview, bug bounty hunter ‘Xel’ walked us through his hacking tools of choice.
- H2C smuggling was named the top web hacking technique of last year.
- Academics are using machine learning to automate the process of exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities.
Additional reporting by Adam Bannister.
Source: https://portswigger.net/daily-swig/latest-web-hacking-tools-q1-2021