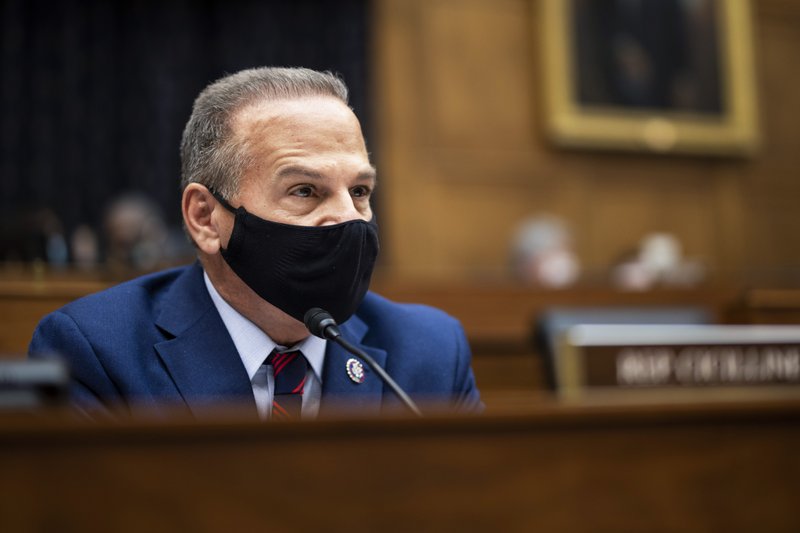
FILE – In this Wednesday, March 10, 2021 file photo, Rep. David Cicilline, D-R.I., speaks during the House Committee on Foreign Affairs hearing on the administration foreign policy priorities on Capitol Hill in Washington. A bill sponsored by Cicilline, which was introduced in March for the third time since 2018, to bolster U.S. news organizations in negotiations with Big Tech has supporters hoping its odds of passage may have improved in a Democrat-run Congress that’s working on overhauling antitrust laws. Cicilline said in prepared remarks for a hearing earlier this month that the legislation would provide news publishers an “even playing field” to negotiate deals with major tech platforms. (Ting Shen/Pool via AP, File)
A congressional effort to bolster U.S. news organizations in negotiations with Big Tech has supporters hoping that third time’s the charm.
The bill, the Journalism Competition and Preservation Act, was introduced in March for the third time since 2018. Its odds of passage may have improved in a Democrat-run Congress that’s working on overhauling antitrust laws.
Australia and other countries have started pushing mechanisms to support news publishers against Facebook and Google, which dominate online advertising. Publishers argue that Big Tech squeezes news organizations out of digital ad revenue and exerts undue control over who can see their journalism.
The bill would offer a four-year antitrust exemption to publishers so they can negotiate as a group with “dominant online platforms.” Facebook and Google get the majority of online ad dollars in the U.S. The measure aims to give publishers better leverage with the tech companies, while only allowing coordination that benefits the news industry as a whole, amid a long-running decline in local news.
Rep. David Cicilline, a Rhode Island Democrat and one of the bill’s sponsors, said in prepared remarks for a hearing earlier this month that the legislation would provide news publishers an “even playing field” to negotiate deals with major tech platforms. The news industry is struggling with falling revenues, shrinking newsrooms and failing publications — which Cicilline and others call a threat to democracy — while Google and Facebook rack up billions in profits.
“This bill is a life support measure, not the answer for ensuring the long-term health of the news industry,” the congressman said.
While the bill has Republican cosponsors in both the House and Senate, some Republicans in the same hearing expressed reservations. Rep. Jim Jordan, an Ohio Republican, said he worried about giving more power to large media companies that would suppress conservatives’ opinions. Republicans often assert without evidence that tech companies censor conservatives and right-wing media.
The News Guild, a union that represents journalists, says the bill would work best with additional provisions to support jobs. It has long objected to media consolidation and criticizes many publishers for impeding unionization and slashing newsroom jobs, particularly at chains owned by hedge funds and private equity firms.
News Guild president Jon Schleuss would like the legislation to require publishers to spend 60% of the revenue won from bargaining to hire more journalists and also support small papers and fund start-ups in “news deserts,” areas where papers have folded, worried that instead it might be spent on things like dividends, stock buybacks and squeezing out higher profit margins.
Microsoft, whose president testified during the hearing, supports the bill. Google and Facebook on Friday declined to comment on the legislation.
In February, however, Facebook took the extraordinary step of banning Australian news from its platform to protest a law that would have required it to negotiate with publishers to compensate them for its use of news content. Facebook lifted the ban once the government agreed to modify the law. Microsoft, meanwhile, has teamed up with European publishers to support measures similar to the Australian law in Europe.
Over the past few years, Facebook, Google, Amazon and Apple have all come under increasing scrutiny from Congress and regulators. The Justice Department, Federal Trade Commission and state attorneys general are suing the internet giants for a variety of antitrust violations, some of which are related to the woes of publishers.
Copyright 2020 Associated Press. All rights reserved.