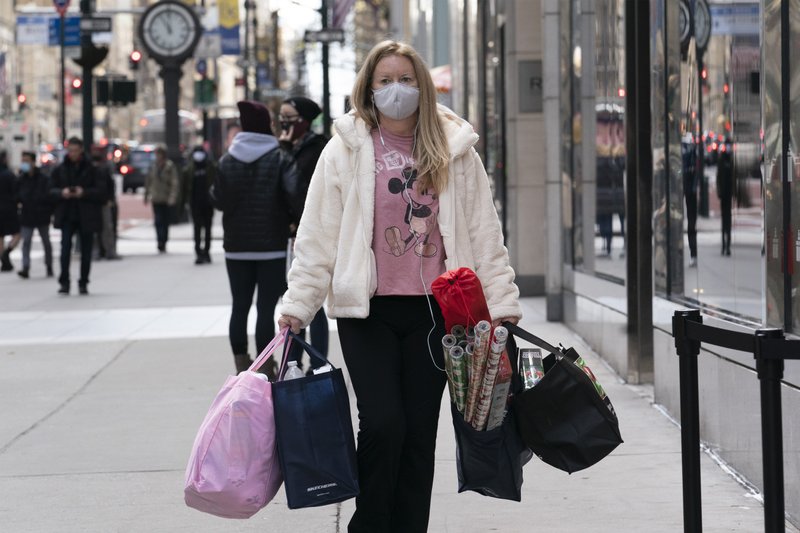
FILE – In this Dec. 10, 2020 file photo, a woman carries shopping bags in New York. The nation’s largest retail trade group is forecasting strong retail sales growth in 2021 that could surpass last year’s pace as individuals get vaccinated and the economy reopens. The National Retail Federation anticipates that retail sales will grow between 6.5% and 8.2% to more than $4.33 trillion this year. (AP Photo/Mark Lennihan, File)
WASHINGTON (AP) — Bouncing back from months of retrenchment, America’s consumers stepped up their spending by a solid 2.4% in January in a sign that the economy may be making a tentative recovery from the pandemic recession.
Friday’s report from the Commerce Department also showed that personal incomes, which provide the fuel for spending, jumped 10% last month, boosted by cash payments most Americans received from the government.
The January spending increase followed two straight monthly spending drops that had raised concerns that consumers, who power most of the economy, were hunkered down, too anxious to travel, shop and spend. Last month’s sharp gain suggests that many people are growing more confident about spending, especially after receiving $600 checks that went to most adults last month in a federal economic aid package.
The government also reported Friday that inflation by a measure preferred by the Federal Reserve rose a moderate 0.3% in December. That left prices up 1.5% over the past 12 months, well below the Fed’s 2% target.
Besides receiving cash payments, many Americans who have managed to keep their jobs have also been saving money for several months. That could bode well for the economy later this year, once consumers feel more willing to spend, vaccinations are more widely distributed and some version of President Joe Biden’s new economic aid proposal is enacted.
Concerns that a strengthening economy will accelerate inflation have sent bond yields surging. On Thursday, the yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury note moved above 1.5% — a level not seen in more than a year and far above the 0.92% it was trading at only two months ago.
The move raised alarms on Wall Street and ignited a deep selloff in the stock market. Some investors fear that rising interest rates and the threat of inflation might lead the Fed to raise its benchmark short-term rate too quickly and potentially derail the economy. The tame inflation figure in Friday’s report from the government shows that so far, price increases are mostly mild.
In testimony to Congress this week, Fed Chair Jerome Powell downplayed the inflation risk and instead underscored the economy’s struggles. Layoffs are still high. And 10 million jobs remain lost to the pandemic that erupted nearly a year ago. That’s a deeper job loss than was inflicted by the Great Recession of 2008-2009.
Still, despite the weakened job market, key sectors of the economy are showing signs of picking up as vaccinations increase and government rescue aid works its way through the economy. The Fed’s ultra-low-rate policy is providing important support as well.
Retail sales soared last month. Factory output also rose and has nearly regained its pre-pandemic levels. And sales of newly built homes jumped in January.
Copyright 2020 Associated Press. All rights reserved.