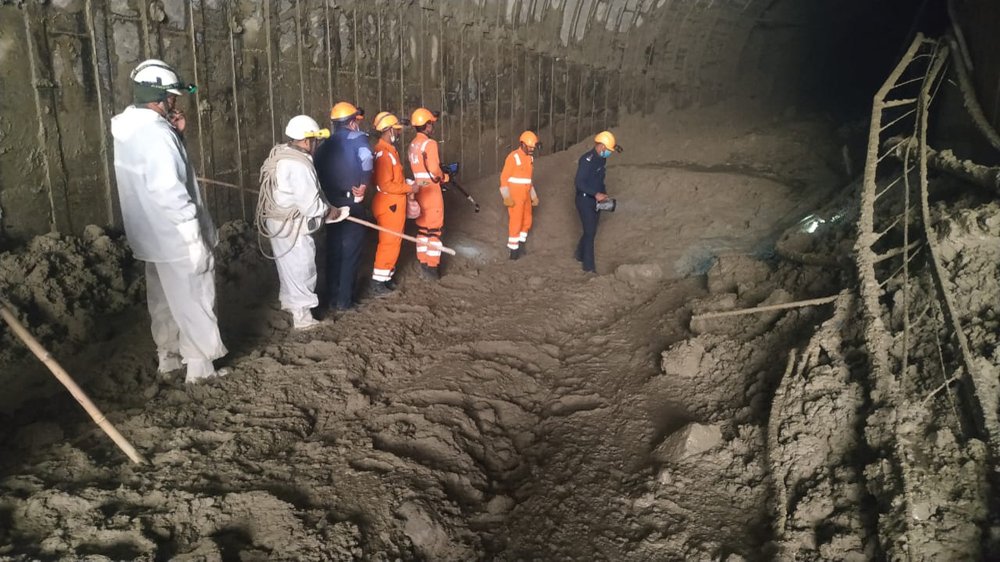
This photograph provided by National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) shows NDRF personnel search for more than three dozen power plant workers trapped in a tunnel after part of a Himalayan glacier broke off Sunday and sent a wall of water and debris rushing down the mountain in Tapovan area of the northern state of Uttarakhand, India, Monday, Feb.8, 2021. (National Disaster Response Force via AP)
JOSHIMATH, India (AP) — Hundreds of rescue workers were scouring muck-filled ravines and valleys in northern India on Tuesday looking for survivors after part of a Himalayan glacier broke off, unleashing a devastating flood that has left at least 31 people dead and 165 missing.
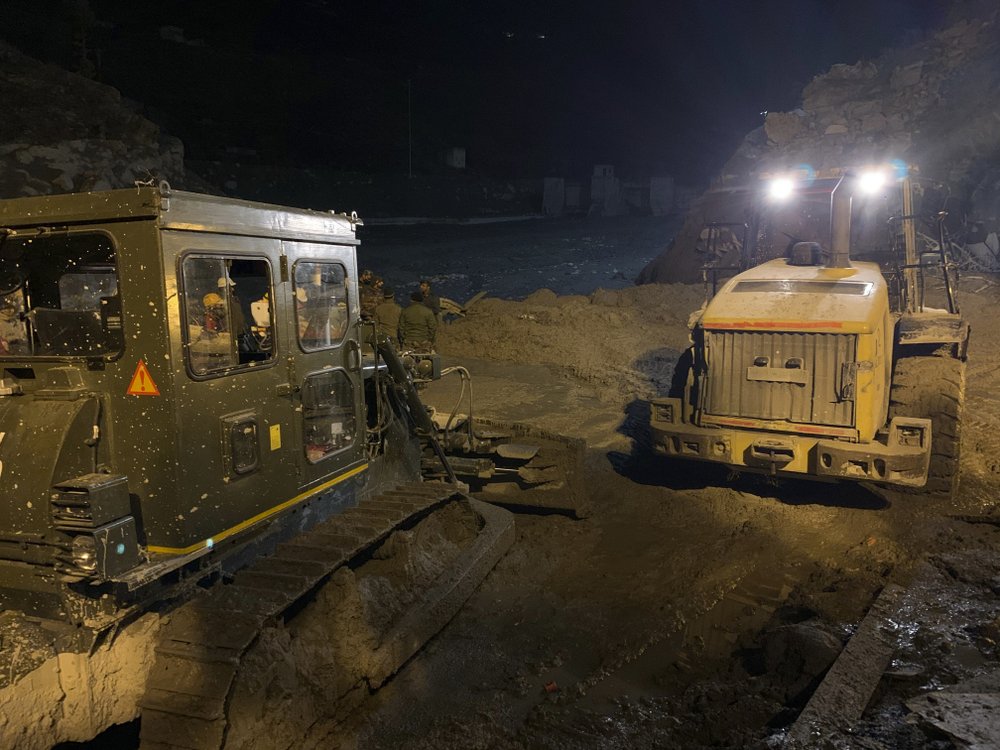
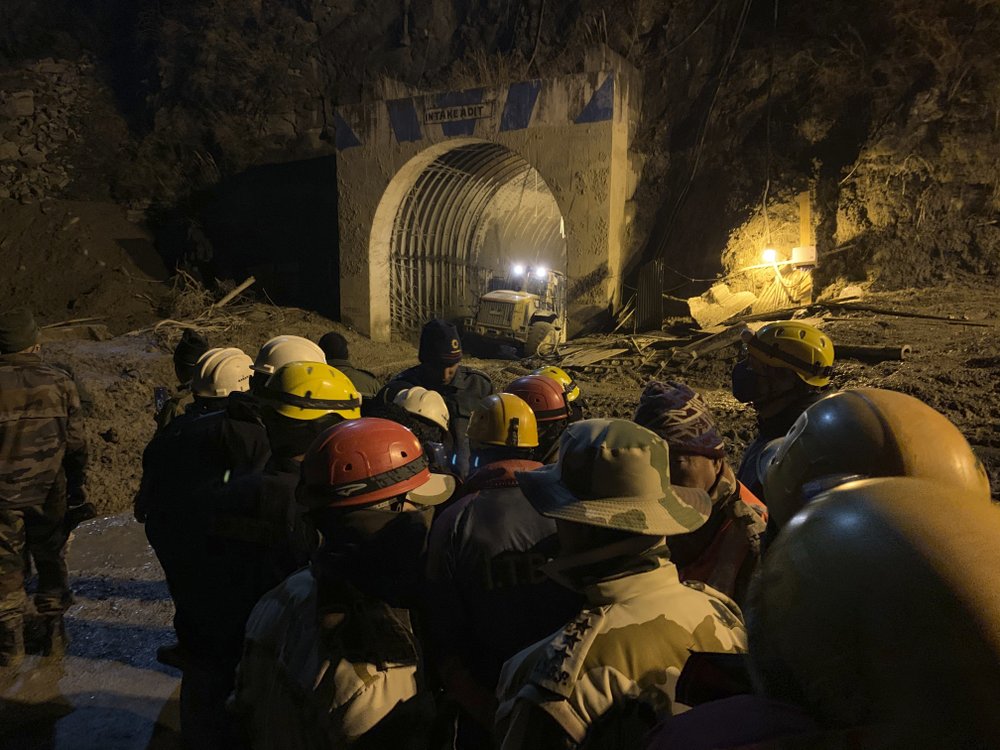
One of the rescue efforts is focused on a tunnel at a hydroelectric power plant where more than three dozen workers have been out of contact since the flood occurred Sunday. Rescuers used machine excavators and shovels to clear sludge from the tunnel overnight in an attempt to reach the workers as hopes for their survival faded.
The disaster was set off when part of a glacier near Nanda Devi mountain broke off Sunday morning. Scientists have gone to the site to investigate what caused the break and the flood — possibly an avalanche or a release of accumulated water. Experts say climate change may be to blame since warming temperatures are shrinking glaciers and making them unstable worldwide.
The floodwater, mud and boulders roared down the mountain along the Alaknanda and Dhauliganga rivers, breaking dams, sweeping away bridges and forcing the evacuation of many villages while turning the countryside into what looked like an ash-colored moonscape.
The flood swept away a small hydroelectric project and damaged a bigger one downstream on the Dhauliganga. Flowing out of the Himalayan mountains, the two rivers meet before merging with the Ganges River.
The power of the roaring wall of water was first noticed by residents of multiple villages perched on the valley slopes.
Rajeev Semwal heard a sound similar to rumbling clouds and then watched the usually blue waters of the Alaknanda turn muddy.
“I understood disaster had indeed struck,” said Semwal, a resident of Tapovan village in Uttarakhand state where the power plant is located.
Semwal’s brother-in-law and younger brother both worked at the power plant. His younger brother was inside the tunnel that was flooded and has not been heard from since.
Most of the missing were people working on the two projects, part of many plants the government has been building on several rivers and their tributaries in the mountains of Uttarakhand state.
Rescuers said it was difficult to predict how long it would take to open the tunnel because of the heavy mud inside, but that they hoped to find people still alive.
“It’s a very big challenge, but we are trying our best and with full strength,” said Aditya Pratap Singh, deputy commandant of the National Disaster Response Force.
Home Minister Amit Shah told Parliament that rescue efforts were on a “war footing.” He said there was no danger of flooding in low-lying areas of the region.
The ecologically sensitive Himalayan region is prone to flash floods and landslides.
More than 6,000 people are believed to have been killed in floods in 2013 which were triggered by the heaviest monsoon rains in decades.
Copyright 2020 Associated Press. All rights reserved.